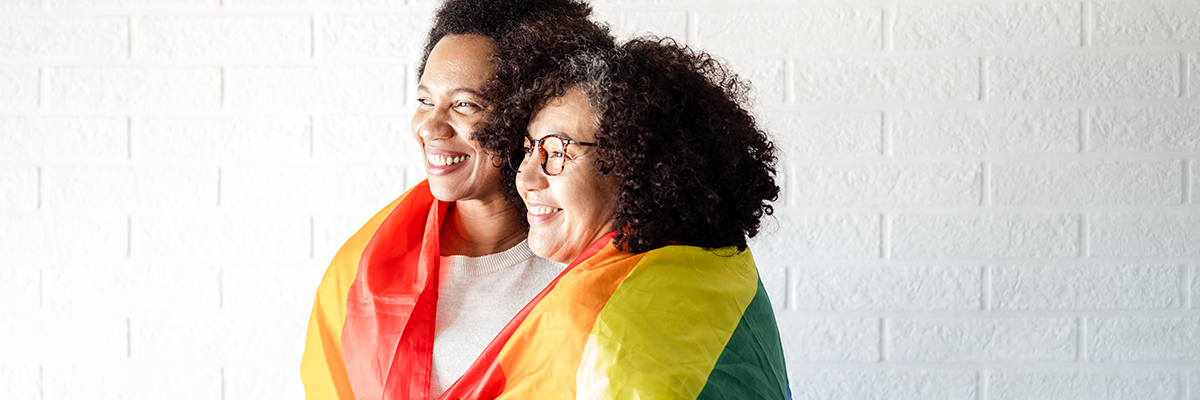
Celebrating Pride Means Supporting 2SLGBTQ+ Mental Health
June is a time for celebrating the diversity of Canada’s 2SLGBTQ+ communities. But it’s also a time to reflect on how we can nurture and support that diversity every day of the year.
The 2SLGBTQ+ community is disproportionately affected by mental health and addiction issues, and it prevents many of its members from living their best lives and reaching their full potential. For families, friends, and caregivers alike, changing the way we think about 2SLGBTQ mental health and addiction treatment and recovery can transform the outcomes.
Progress and challenges
There is much to celebrate during this year’s Pride Month. As of 2023, Canada is home to one million individuals who identify as 2SLGBTQ+, which represents 4% of the total population aged 15 and older. Three-quarters of Canadians support same-sex marriage, and 61% say they support LGBT people being open about their sexual orientation and gender identity with everyone. Just last year, the federal government unveiled a five-year, $100 million plan to support 2SLGBTQ+ communities across the country.
Yet in some ways, 2SLGBTQ+ visibility and acceptance have never felt more fragile as there is often backlash. Between 2019 and 2021, hate crimes based on sexual orientation rose nearly 60% to reach their highest level in five years.
More than ever, we need to make an effort to understand, celebrate, and make room for queer lives and identities, and that’s especially true when it comes to supporting 2SLGBTQ+ mental health and addiction treatment.
 The cost of being queer
The cost of being queer
In a perfect world, people of all genders and sexual orientations would be given equal opportunities to thrive. But the reality is that 2SLGBTQ+ Canadians still face multiple barriers to health, wealth, and wellbeing.
Many 2SLGBTQ+ Canadians live with the trauma caused by secrecy, stigma, discrimination, and fear. In addition to being the target of hate crimes, they are also more likely to experience financial distress, homelessness, and housing insecurity than heterosexual Canadians. Canadians who are 2SLGBTQ+ also have fewer job opportunities and earn significantly less than straight, male counterparts and experience frequent microaggressions at work. A lack of access to medical care, suboptimal healthcare experiences, and poorer health outcomes also diminish quality of life for queer people.
A mental health crisis
In the face of so many challenges, it’s unsurprising that the queer community sees a higher proportion of mental health and addiction issues.
Courtney Sullivan, Addiction and Mental Health Therapist and Support Coordinator at Homewood Health Centre, which is located in Guelph, Ontario and one of the largest mental health and addiction facilities in Canada, provides both outpatient and inpatient treatment for addiction and mental health. They work with clients who identify as queer, including individuals who may be experiencing homelessness, job loss, trauma, addiction, and a range of mental health issues.
“There is a lot of stigma towards the queer community,” they explained. “A lot of people have their families disown them or kick them out or withhold family support. A lot of queer youth, in particular, end up in the shelter system, which exposes them to trauma and substance use, and their mental health can get a lot more complex.”
Research shows that 2SLGBTQIA+ Canadians are seven times more likely to abuse drugs or other substances and five times more likely to have mental health issues. Sexual-minority Canadians are also approximately 25% more likely to contemplate suicide (40% vs. 15% for the general population) or have a mood or anxiety disorder (41% vs. 16%).
Treatment challenges
Not only do 2SLGBTQ+ have a higher likelihood of developing mental health issues and addictions, but their treatment journey is complicated by systemic ignorance and discrimination in the healthcare system.
According to a 2019 survey, 59% of nonbinary people were misgendered daily and only 47% felt comfortable discussing non-binary health concerns with their primary care provider. One in three said their primary healthcare provider had no knowledge about trans/non-binary health needs, and one in four did not have access to in-person spaces specific for non-binary people.
“There’s a large amount of queer people who don’t actually disclose their queerness to their health care providers,” said Sullivan. “The medical system doesn’t have the greatest history,” they continued, pointing out that as recently as the 1970s, homosexuality was classified as a mental disorder.
“People who do disclose to their doctors are often put in a position where they have to educate them about how healthcare should be delivered, which puts a huge burden on the queer community.”
It’s even more complicated for people with an intersectional identity that combines queerness with another identity that puts them at a systemic disadvantage, such as being a person of colour or an Indigenous person.
“Recovery programs and agencies and organizations really need to show their support to the queer community and signal that they are seen, that their experiences are respected, and that the facility is open to work with you,” Sullivan said.
While Sullivan advocates for big changes in the healthcare system, including hiring for diversity and developing organization-wide policies that reflect diverse perspectives, they also believe that small things can make a big difference. As an example, they described a recent situation when they brought a suicidal trans client who didn’t feel healthy at home to the hospital. Asking for help took tremendous courage, but the client was deadnamed three times in a row during the intake process, which almost made them reject treatment. (Deadnaming occurs when someone calls a transgender or non-binary person by the name they used before they transitioned. While deadnaming may be unintentional, it can feel stressful and traumatic because it questions or invalidates a person’s gender identity.)
“The hospital is supposed to be a healthy space, and most healthcare workers are well-intentioned, but systemic homophobia and racism can come out through the policies and the way things work,” they said. “Something as simple as restructuring medical charts so that gender information and preferred pronouns are easily available at a glance can change the experience. Or have care providers identify their pronouns, which is kind of like offering an invitation for that person to give you theirs too.”
S upporting 2SLGBTQ+ mental health
upporting 2SLGBTQ+ mental health
If you are a friend, partner, or family member of a 2SLGBTQ+ person exploring treatment options or actively in treatment or recovery, you can play an integral role in supporting their mental health and resilience.
For Sullivan, these communication tips can help to ensure they feel heard, seen, and supported throughout the journey.
Let them lead. “Your loved one might have a substance use issue, but if they’re not ready to hear it, don’t force it on them,” said Sullivan. “When people get scared, they make threats, like, ‘You need to get sober or else!’ But that ruins the opportunity and the trust.” Instead, let that person decide what they need and set the pace for treatment and recovery.
Keep an open mind. “Come at things with empathy and compassion. Listen to that person. Try to understand why they’re making the choices that they do.” Sullivan pointed out that for some members of the 2SLGBTQ+ community, the use of stimulants is an important part of their lifestyle and sexuality. “It all comes back down to the impact that the person’s substance use has on their life, and what that person identifies as being problematic.”
Respect their experience. “The trauma and the experiences that queer people have are different,” Sullivan explained. “Even if you’re cisgender and you get kicked out of your home, it’s still a different experience than someone being kicked out of their house because of who they are.” Respecting those differences can go a long way toward creating a space for authenticity and healing.
 Pride in mental health
Pride in mental health
Pride Month is a time to celebrate the queer community and bring attention to the challenges it continues to face. The elevated risk of mental health and addiction issues is an important part of the story, and one that Homewood Health Centre and other mental health and addiction facilities in Canada are highlighting this year. We all have a role to play in supporting and protecting the mental health of 2SLGBTQ+ individuals, and that role goes beyond raising the rainbow flag.
“We’re having a flag-raising ceremony in honour of Pride here at Homewood, but that’s just the first step,” said Sullivan. “It’s about creating intersectional representation. You want people of colour working in your organization, you want Indigenous perspectives, you want queer perspectives. Be willing to hear the experiences of the people you employ and the people you support. Find out what it is that they’re looking for.”
Learn more about LGBTQ+ mental health.
Learn how to support children who identify as LGBTQ2+.
